Structure and operation of the electric power steering column

Today it is impossible to imagine the steering mechanism of a car without an amplifier. And this applies not only to powerful SUVs or business-class sedans. Now even drivers of compact small cars began to appreciate the comfort of steering. However, under the bonnet of such cars there is not often a lot of space for installation of a steering rack with hydraulic or even electric booster. But it is not a problem - it is possible to place the assistant to the driver even in the steering column. What advantages has such a scheme and how it is realised, let's consider the example of a popular car Volkswagen Lupo 1.2 TDI 3L 1999-2005 years of manufacture.

Features and benefits of an electric steering column
It should be noted at once that the electric steering column cannot be considered only as a compromise variant of steering amplification. Such a scheme, among other things, has its own significant advantages, namely:
- controls input and output signals, as well as the operation of other components of the steering mechanism;
- provides a clearer sense of road contact to the driver;
- helps to align the steering wheel in a straight position;
- increases steering control based on actual driving conditions;
- operates only when the driver turns the steering wheel, not consuming power on straightaways.
- The last factor contributes to the fact that such an electromechanical system is very different in parameters from a traditional hydraulic system. According to research by Volkswagen, the differences are as follows for the Lupo model:
| Hydroboost | Electric speaker |
Weight | 16.3kg | 11.3kg |
Energy consumption in the urban cycle on the motorway | 400 watts | 25 W |
800 W-1 kW | 10 W | |
Additional fuel consumption compared to conventional mechanical steering rack in litres per 100 km | 0.1 litre (100 ml) | 0.01 litre (10 ml) |
Not least because in a hydraulic power steering system all components of the system are installed after the steering PTO shaft, whereas in an electromechanical power steering system the power steering is installed before the PTO shaft.
.png)
.png)
Another major plus is that the power steering in the speaker is housed in one compact unit, so it doesn't need long, complicated wiring. And finally, perhaps most valuable for drivers - because the electric motor that amplifies the rotation drives the worm gear right next to the steering wheel, the driver has direct steering feel, which is the same feedback to the road as if there were no power steering.
Design of the electric power steering column
.png)
The main components of the upper part of the steering mechanism in this arrangement are shown in the figure
- turn indicator and windscreen wiper switches,
- steering column housing,
- worm gear,
- steering column electronics control unit,
- steering gear driveshaft.
In addition, very important sensors are installed inside: steering position and steering torque sensors.
And this is what the electric steering column looks like in a cross-section of the entire front of the car:
.png)
Now let us elaborate on the components of the steering column, which is equipped with electric power steering. They can be divided into two groups:
Electric.
Mechanical.
The first group includes the following electronic components:
- electric motor and its coupling;
- EPS control unit;
- steering torque and steering position sensors in a common housing.
The second group is used in all, not just electromechanical, columns. These are:
- shafts: steering and driveshaft;
- the steering column housing, which is height adjustable;
- worm drive with worm and pinion;
- intermediate spindle;
- torsion bar.
This tie rod is the central component of an electrically assisted steering column. The torsion bar mechanically connects the intermediate spindle to the worm drive shaft. This allows the two parts to rotate oppositely by a small angle. This is sufficient for the system to recognise the start of steering.
.png)
The gimbal shaft consists of two forks that are connected to a short telescopic arm. It compensates for the length of the height adjustment mechanism and protects the driver and passengers in the event of a frontal collision. If the driver raises the lever upwards during adjustment, the lever becomes shorter, which reduces the distance between the steering wheel and the steering mechanism. If the opposite is true, the telescopic lever lengthens. The adjustment range of the Volkswagen Lupo is 39 mm.
The worm gear is in the aluminium gearbox housing together with the electric motor. The worm on the motor shaft meshes with the gear on the steering shaft, which allows the steering wheel rotation to be amplified directly almost where the driver does. The motor shaft is connected to the worm shaft by a flexible rubber coupling, so that the starting torque of the motor is transmitted as gently as possible. The electric motor has a power output of 720 W and develops a torque of 2 Nm. The electronics are designed to have an extremely short response time so that it reacts as quickly as possible to steering movements.
.png)
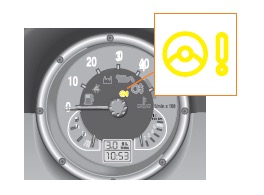
The steering position and steering angle sensor housing is mounted above the gear. The former is co'ed with the worm gear shaft. It registers the current position of the rudder or its blocking. The second is connected to the torsion beam. It calculates the angle of rotation of the torsion bar in relation to the intermediate spindle. The control unit calculates the torque based on this signal. If the calculated torque exceeds a value of 0.01 Nm, the control unit decides whether the steering needs to be reinforced. <Also bolted to the worm drive housing is a frame in which the electronic power steering control unit is installed. It calculates the necessary assistance to the driver based on the data received from the sensors and taking into account the speed of the vehicle. The sensor housing is wired to the control unit using a 6-pin connector. If the control unit detects a fault in the power steering system, it switches on the steering indicator light in the instrument cluster.
How electromechanical steering is enhanced
The driver begins to turn the steering wheel. At the same time, the torsion bar rotates. The torque sensor rotating with the torsion bar supplies the control unit with signals indicating the magnitude and direction of rotation of the steering torque. The unit calculates the required assistance on the basis of these signals and activates the electric motor. The combination of the torque acting on the steering wheel and the assist torque constitutes the effective torque acting on the steering gear.
If the driver increases the torque applied to the steering wheel, the electric motor increases the torque. If it decreases, the torsion bar torsion decreases. As a consequence, the steering torque sensor provides a smaller signal to the control unit. <When the driver releases the steering wheel during cornering, the tension on the torsion bar is released. At the same time, the electronics deactivates the electric motor, as torque assistance is no longer needed. However, if the steering position sensor detects that the vehicle is still not travelling straight, then the electric motor is activated so that the steering wheel is actively returned to the straight position.
Repairing a power steering column
Although the described design is quite reliable, time and active use often lead to malfunctions. The parts that are most likely to fail are:
- Plastic sensor rings;
- the sensors themselves;
- the driveshaft cross members.
Although the electric steering column is less vulnerable than other types of power steering because it is located inside the cabin, it too can suffer from corrosion. Sensor and control unit contacts can oxidise, and even the splined joints of the mechanical components.
Unfortunately, the company-manufacturer does not provide replacement of separate components of the electric amplifier - in its opinion, the whole column should be changed completely. But not all car owners can afford it.
That is why we invite those who have problems with such units to the STS workshop. Our qualified specialists are able to repair any power steering unit in the shortest possible time at an affordable price.
That's why we invite those who have problems with such units to STS workshop.