Why the Steering knuckle gets damaged and how it is repaired

Today, we'll provide an educational program on the ball joint: to which system it truly belongs, how and why it breaks, and how these malfunctions are rectified.
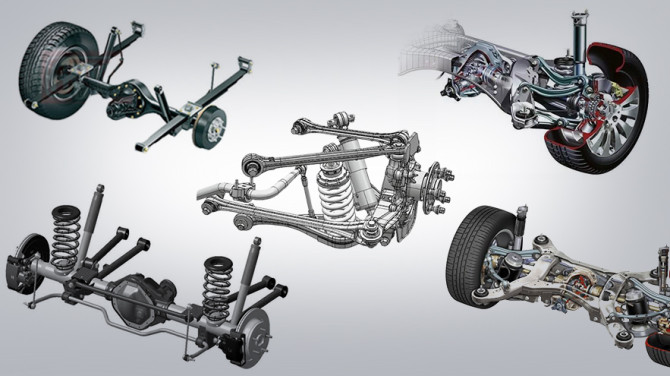
Front Suspension Ball Joint
The ball joint is a key element of the front suspension of a car; it turns the wheels. The effort is transmitted from the steering wheel through the steering system to the ball joint, which then turns the wheels at the desired angle.
Since it actively participates in the steering system, it belongs to the chassis system, but it includes elements of the steering control.
Principle of Operation
The ball joint interacts with a set of components:
- Strut: This is the shock absorber unit that connects the body to the wheels.
- Ball Joints: The lower or upper point of support and attachment of the ball joint, which rotates around its axis. Turning the wheel is impossible without a ball joint.
- Tie Rod Ends: The force is transmitted from the steering wheel to the steering mechanism, then to the tie rods, and from them to the ball joint.
- Hubs: The central part of the wheel, which has holes for the shaft to transmit torque. The hub has either a splined profile or a keyway for transmission of torque.
Common Faults
Ball joints rarely break, mostly due to mechanical damage: in accidents or from hammer blows when a mechanic incorrectly removes the hub bearing.
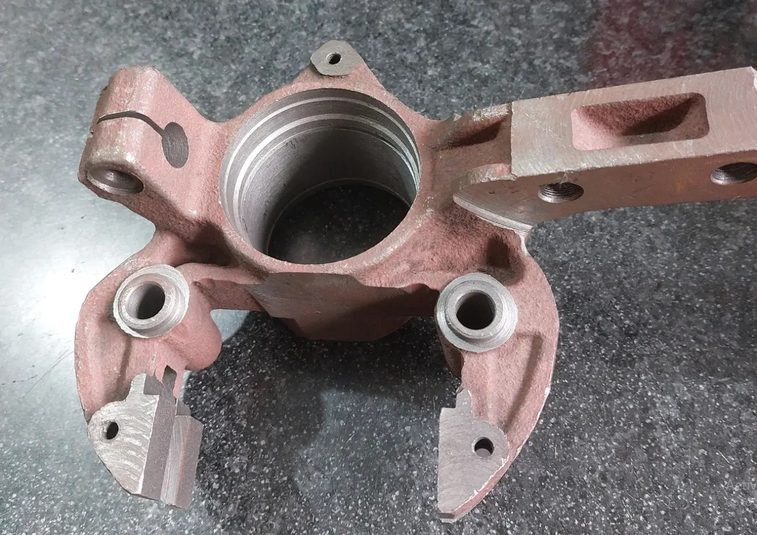
1. Groove Wear in Bolt Holes of the Ball Joint: These are the holes through which it connects to the support and other elements.
Signs: Wheel knocking during movement on uneven roads – the suspension knocks on pits. If you shake the wheel, you can detect play in the ball joints.
How to Repair: A lathe operator at an auto repair shop machines the damaged groove on a lathe and then cuts a new groove.
2. Mechanical Wear: Over time, the seating sockets and bushings of the ball joints, hub bearings, tie rods, and tie rod ends break down.
Signs: When the hub bearing wears out, there is noise and play in the wheel during movement.
How to Repair:
- At an auto repair shop, the broken bushing is pressed out on a hydraulic press, and a new one is pressed in using the same method. The same procedure applies to the hub bearing.
- If a ball joint and its seating socket have play after pressing, a bushing is pressed in. A bushing is a sleeve or nut that, in addition to an internal groove, has an external groove for a larger diameter thread connection. This bushing can be purchased or ordered, or turning can be done by a lathe operator, who will machine the seating socket to a larger diameter.The upper support is usually screwed on through the pin of the tie rod end.
- Steering rods and tie rod ends need to be replaced.
3. Crack in the Ball Joint
Signs: You will see a crack on the ball joint; if the crack is deep, the ball joint breaks and the wheel may come off.
How to Repair: The ball joint is made of steel or cast iron. Some mechanics offer a welding service for a cracked ball joint. If the joint is cast iron, welding won't help.
Considering that this element bears a tremendous load during driving, welding work on it can be an extremely unreliable solution. We recommend not risking your safety and going to a specialized auto repair shop, where the ball joint will be replaced on your car.