Signs of steering rack damage: how to recognise

A reliable steering system is one of the main components of active vehicle safety. After all, it is extremely important for drivers to have reliable control over the vehicle's movements, especially at high speeds or in difficult road conditions. Therefore, when symptoms of a damaged steering rack appear, it is important to immediately understand how to recognize a damaged steering rack so as not to risk your life and your car. Unfortunately, malfunctions of these components are not uncommon, as they are constantly subjected to stress and external factors. From potholes on the road to the simple aging of parts due to friction.
How to understand what has happened to the steering mechanism
Usually, drivers only start paying attention to the steering when it becomes noticeably uncomfortable or dangerous to drive. But most signs can be noticed earlier if you know what to look for. This will help you avoid serious problems with vehicle control and save on expensive repairs.
Here is a detailed table that will help you quickly understand what is happening with your steering rack:
| Sign or symptom | What it could mean | Consequences if ignored |
| The most common sounds of a damaged steering rack are knocking, squeaking, or grinding when turning | Wear on the gear teeth, bushings, steering rods, or damaged sealing rings | Further damage, risk of steering wheel lockup |
| The steering wheel turns jerkily or with noticeable effort | Problems with the power steering pump, fluid leak, malfunction of the distributor | Complete failure of the power steering at a critical moment |
| Play in the steering rack symptoms — turn the steering wheel and the wheels respond with a delay | Wear or loosening of components in the steering gear, including in the steering racks | Unstable trajectory, «floating» of the car |
| Fluid leak visible at the parking spot | Cracks in the rack dust covers, damaged seals, weak sealing rings | Pressure drop, damage to the booster pump, risk of system failure |
| The car pulls to one side even on a level road | Deformation of the rail after impact or uneven wear | Additional load on tires and other chassis components |
If you experience these or similar symptoms, you should check the condition of the steering rack, even if the signs only appear occasionally. Diagnostics and, if necessary, repairs will help you avoid serious and expensive problems in the future.
Causes of steering rack damage
Every steering rack operates in fairly harsh conditions: it is responsible for transmitting force from the steering wheel to the wheels, which means it affects the precision of the entire vehicle's steering. Therefore, there are many reasons for its wear and tear, and they often combine, accelerating the destruction of the mechanism.
Why does steering damage occur in the first place? The symptoms, like their causes, are quite varied and depend on both operating conditions and the design features of the vehicle model:
- Regular impacts of the wheels against potholes or curbs cause microdeformations of the shaft, gear elements, and bushings, which over time lead to backlash and squeaking.
- Aging and drying out of sealing rings, causing fluid leakage and, subsequently, overheating and wear of the power steering pump.
- Incorrect or untimely replacement of power steering fluid, use of cheap analogues.
- Accumulation of moisture and dirt under the rail dust covers, leading to corrosion and faster wear of metal parts.
- Age of the car: even without aggressive use, the rack is subject to wear simply due to time and mileage.
That is why it is so important to have your car checked regularly, even if everything seems to be fine.
Typical steering rack faults
Even without an obvious accident, a malfunction can occur due to local defects or design flaws. The most common problems are as follows:
- Incorrect rack adjustment leads to uneven gear contact.
- Wear on the side support weakens the rack clamp, causing knocking.
- Wear on the distributor bearings causes the spool to stick and increased noise.
- Ring wear forms a groove in the housing, causing leakage.
- Wear of the inner wall of the rack housing affects the smoothness of the gear.
- Wear on the spool and torsion bar disrupts the balance of fluid flow, causing the booster pump to work under load.
- Electrical booster malfunctions often manifest as jerks and heaviness when turning.
It is these defects that eventually form the classic symptoms of a broken steering rack, and sometimes even destroy the entire assembly.
How much does it cost to replace and repair a steering rack?
The cost of repairing or replacing a steering rack can vary significantly, as much depends on the specific type of failure and the design of the particular car model. Ultimately, the savings here are often questionable, as excessive cheapness means the use of poor-quality parts or dubious services.
The budget for repair or replacement depends heavily on the type of rack (with power steering, electric power steering, or mechanical), the car model, the cost of original parts, and the complexity of the work.
| Service | Approximate price | What is usually done |
| Repair and regeneration of the steering rack) | From 70 PLN | Replacement of seals, bushings, restoration of gear teeth |
| Diagnostics and repair of the steering gearbox | From PLN 130 | Restoration with complete disassembly, replacement of faulty parts, testing on a test bench |
| EPS diagnostics and repair | From PLN 130 | Restoration and calibration using professional equipment |
Remember that a damaged steering rack can have much more serious consequences. The risk of getting into an accident due to steering failure is priceless and far outweighs any savings.
The dangers of driving with a damaged steering rack
Some people may naively think, “I'll drive a little longer and then get it repaired,” but this is too risky. With a faulty steering system, any sharp turn or emergency maneuver can end tragically. Here are some real dangers:
- A sharp deterioration in driving comfort: vibrations in the steering wheel, tight or jerky steering, squeaking, noise.
- Accelerated tire wear and wheel misalignment, as play destroys the correct suspension geometry.
- Risk of complete failure of the unit when overtaking or turning at high speed.
- Additional problems with vehicle control, which become noticeable on wet or slippery roads.
- Ultimately, damage to adjacent parts: power steering pump, tie rod, gears in the mechanism.
It is much cheaper and less stressful to repair the steering rack at the first signs of a malfunction.
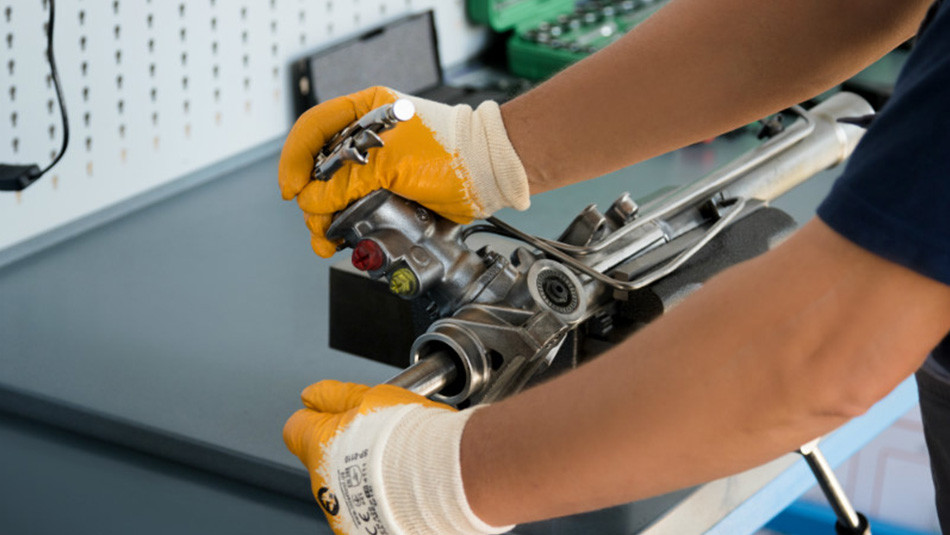
Self-diagnosis and a visit to a mechanic
It is not always necessary to wait until the steering wheel starts to behave strangely or turn with a crunch — problems can often be detected at an early stage. However, a self-inspection does not always guarantee the detection of underlying problems, as they may be hidden in the gear mechanism or gears, which requires disassembly of the unit.
Is it possible to independently identify the symptoms of a worn steering rack or suspect a worn steering rack, as well as the symptoms of other problems? Partially, yes:
But the best option is to immediately contact a specialist who will check the condition of the unit, the dust covers, the tie rod, the seals on a lift, and make adjustments or repairs if necessary. Remember: even a minor malfunction can quickly turn into a serious breakdown if not fixed in time.
- Rock the steering wheel while the engine is off. If you feel play that wasn't there before, that's a warning sign.
- Look under the car in the parking lot — is there a leak? It may be leaking through the sealing rings.
- Turn the steering wheel left and right and listen. Do you hear a knocking or grinding noise? These are symptoms of a damaged steering gear.