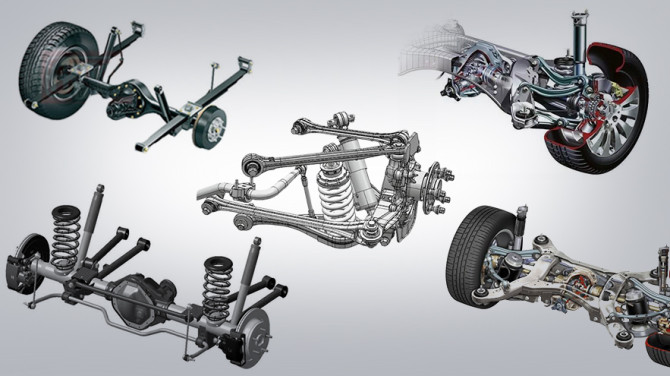
Malfunctions in the steering system

The steering system is a complex and balanced assembly of interconnected mechanisms and components. When something in the vehicle's steering system is malfunctioning or not working correctly, it becomes challenging for the driver to control the vehicle, increasing the risk of accidents.
It is concerning that steering system failures account for 7% of road accidents in Poland annually. The root cause of this issue is often drivers not being aware of signs indicating steering system malfunctions.
To improve this situation and warn against unexpected road problems, this article explains:
- How to recognize when the vehicle's steering system is faulty.
- How to identify the type of failure and locate the malfunctioning device or its part.
- What to do when the vehicle's steering system is not functioning properly.
Classification of Failures Based on Characteristic Features
Loss of Steering Power:
- Wear of the torque pair of the hydraulic power steering pump – replace the torque pair or the entire mechanism.
- Low fluid level in the tank – check the hydraulic system's integrity, replace worn components, and fill the tank to the optimal level (between MIN and MAX).
- Wear of the peripheral housing of the distributor – reaming and bushing the distributor housing can help.
- Wear of the coil in the distributor mechanism – replace the coil or the distributor.
Loss of Power Assistance when the Steering Wheel is in the Center Position:
This symptom indicates a hydraulic shock. A hydraulic shock occurs during driving on uneven terrain and bumpy roads. It involves the piston of the rack hitting the cylinder housing, creating a circumferential gap on the inner surface of the distributor housing.
The solution is to replace the distributor housing or the entire unit.
Wheels Delay in Responding to Steering Movements:
- Worn central teeth of the rack gear or a worn worm shaft in the distributor – replace the worn rod/worm or the entire steering rack assembly.
- Displacement of the worm gear – incorrect adjustment of the gearbox; adjust the position of steering rack elements.
- Worn steering shaft U-joint – replace the worn joint or the entire shaft.
"Biting" and Sticking of the Steering Wheel, with Audible Squeaking during Turns:
Deformed rack gear (bent after an accident) – replace the rack bar or the steering rack.
Worn relief valve of the steering system pump, worn valve seat – replace the valve or the entire pump.
Excessive tightening of the side pressure piston, pressing the rack to the worm shaft excessively – adjust the position of elements.
Loss of Power Assistance during Turning the Wheels in One Direction:
This symptom indicates wear of the peripheral area in the distributor housing. The problem arises in the gearboxes due to natural wear and tear of the distributor housing.
The solution is reaming and bushing the distributor housing.
Steering Wheel Doesn't Return to the Center Position or Returns Too Late:
The problem occurs when the steering mechanism is incorrectly adjusted, specifically over-tightened, and the steering mechanism elements are too tightly compressed. To solve this problem, loosen the side loading piston and adjust the position of the rack bar and "worm" of the distributor mechanism.
Steering Wheel Spontaneously Turns and Wobbles from Side to Side:
- If the steering system has hydraulic assistance, the steering rack bar is damaged in the distributor mechanism – replace the rack bar or the pinion.
- If the steering system has electric assistance, the issue is with the power assistance sensors – calibrate or replace the power assistance sensors.
Heavy Steering during Fast Turns:
- Air has entered the system – check the condition of sealing elements, replace ineffective elements.
- The pump does not generate the required pressure – if the issue is with the torque, replace the rotor and stator, and if it concerns the entire pump, replace the entire unit.
- The drive belt is improperly tensioned – adjust the belt tension and the position of drive pulleys.
Driver Hears Unusual Noise, Whistling, Buzzing, or Creaking:
- Air has entered the system – check the condition of sealing elements, replace ineffective elements.
- Rotors or bearings of the power steering pump are worn – replace worn elements or the entire assembly.
- The hydraulic oil tank filter is clogged – replace the tank.
- Hoses are deformed – replace unusable elements.
- The pump does not generate the required pressure – if the issue is with the torque, replace the rotor and stator, and if it concerns the entire pump, replace the entire unit.
- The drive belt is loose or worn – adjust or replace the belt.
The fluid level in the hydraulic oil tank has dropped – check the integrity of the steering system, replace worn components, and top up the fluid to the optimal level (between MIN and MAX).
Constantly Decreasing Fluid Level in the Steering System:
- Steering rack or pump sealing elements are worn – replace ineffective elements.
- One of the hydraulic lines is leaking – replace sealing elements and damaged parts.
Steering Wheel Vibrates when Driving over Bumps:
- Wheels are not balanced – adjust the wheels.
- Wheel alignment is imbalanced – adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or Stiff Steering Wheel and/or Rattles:
- Worn suspension system components – replace ineffective elements.
- Worn steering U-joint – replace worn parts or the entire shaft.
- Improper adjustment of the steering rack – adjust the position of the rack and worm shaft.
Rattling of the Steering Rack and Simultaneous Vibration of the Steering Wheel:
- Incorrect adjustment of the steering rack – adjust the position of the rack and worm shaft.
- Suspension system components are worn – replace ineffective elements.
- Gears in the steering gear are worn – replace the rack bar and worm gear.
- Tie rods and steering linkages are loose or worn – replace worn and damaged parts.
CAUTION! Upon detecting a steering system failure or noticing characteristic signs of steering system malfunctions, it is crucial to contact a specialized workshop dealing with steering systems. STS Workshop Advantages:
- Professional, qualified, and experienced specialists with a narrow scope of operation. Each mechanic specializes in a specific type of unit and knows everything about malfunctions in that unit group.
- Specialized and precise equipment for diagnostics and repair.
- Full range of services related to the repair and diagnostics of steering systems.
- Quality assurance. The warranty period for all services is six months or 20,000 kilometers.
Let's explore the common failures repaired by the specialized STS workshop.
Repair of the Distributor Mechanism:
In the case of a distributor mechanism failure, the damaged assembly is first checked using diagnostic devices. The technician identifies the cause of the failure, disassembles the device, and replaces the components. Distributor components are replaced as needed.
If the distributor rack bar is corroded, but the corrosion depth is minimal, the lathe operator grinds the part. If corrosion has penetrated deeply into the rack bar or the part is heavily worn, the worm shaft is replaced with a new one.
If the distributor housing has peripheral wear, the lathe operator reaches the inner wall of the distributor housing using a boring machine and presses in a thermal cover. This process is referred to as "bushing the rack body."
Recovery of the Steering Rack Bar
Corrosion of the steering rack bar is a common problem in Polish cars, caused by high air humidity. Moisture and dirt enter the rack shaft through gaps in the rubber covers. As a result, the bar rusts, and the steering mechanism fails.
Before repairing, the mechanic disassembles and checks the condition of all steering rack components, then replaces damaged elements. If the damage to the rack is minor, the lathe operator grinds the element on a lathe. If the corrosion is deep, the rack bar is replaced with a new one. If corrosion has damaged the rack housing and other components, it is more cost-effective to replace the entire unit.
Recovery of the Steering Rack:
- Recovery of the rack is necessary when the rack bar teeth are worn, and there is significant play between the rack bar and the worm in the pinion. In this case, the mechanic:
- Disassembles the device using specialized tools.
- Replaces components.
- Replaces the worn rack bar and the worm of the pinion.
- Checks the condition of the distributor mechanism, replacing worn components or the entire pinion if necessary.
- Assembles and tests the repaired unit on a diagnostic stand.
Adjustment of the Steering Rack
If the rack bar and pinion steering rack is loose, but the distributor rack and worm are functional, the likely cause is faulty steering rack adjustment. The mechanic checks the condition of the mechanism, and if other elements are undamaged, adjusts the position of the rack using the side loading piston. Finally, the device is checked for clearances and leaks using specialized equipment.
Repair of the Hydraulic Power Steering Pump
Failures of the power steering pump affect the entire steering system. If the pump is damaged, the entire unit is removed from the vehicle, disassembled, and the condition of all pump components—torque, relief valve, thrust bearing, upper and lower oil inlet plates, and sealing elements—is checked.
Damaged parts are replaced, and then the pump is reassembled and tested on a hydraulic stand that simulates the car's operation. If the damage is severe, and the device is not suitable for repair, the mechanic will propose replacing the pump with a new one.