BMW 5 Series F10/F11/F07 Steering Rack Repair at STS
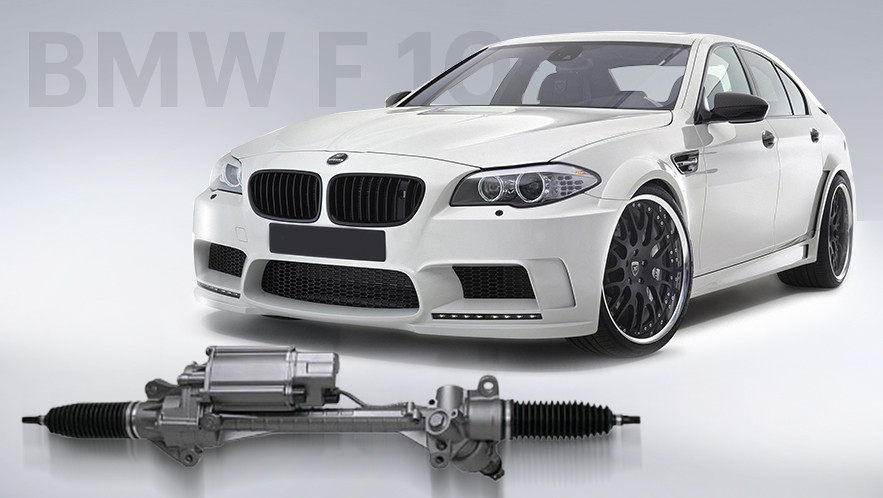

BMW F10 is the internal index of the 5th series of BMW, manufactured from 2009 to 2016. This family also includes:
- F11 – station wagon (Touring);
- F07 – Gran Turismo (liftback with an extended wheelbase).
All these cars are built on a common platform with extensive use of electronic systems, in particular electric power steering (EPS), which replaced hydraulic systems.
Key features include: all-aluminium front suspension, adaptive systems (Variable Sport Steering, Dynamic Drive), modular electronics (FlexRay) and extensive CAN communications.
Types of steering mechanisms on the BMW F10
All BMW F10, F11 and F07 models were equipped with electric power steering (EPS) with belt drive. For BMW, this was essentially the second generation of EPS, the first being the electric racks installed on cars with body codes beginning with E: 1-series (E81/E82/E87/E88), 3-series (E90/E91/E92), X-series x1 (E84) and others. Prior to that, the company used hydraulic systems, including electronically controlled ones.
There are three main types of F10 racks:
- Standard EPS. A basic rack with electric power steering, installed on most models without a sports package. It has a fixed gear ratio, an electric drive unit with a motor, a reducer and an encoder.
- Sport EPS (SA2VL). A modified rack with a variable ratio. It uses a non-standard tooth profile in the central area of the rack, which provides a different response to steering depending on the steering angle.
- Active EPS (P2VH). A system with an active steering mechanism. It has an additional electric motor that can change the position of the rack independently of the driver's steering wheel rotation — for example, during stabilisation manoeuvres or steering in adaptive systems.
All racks have a belt drive that connects the electric motor to the worm gear. The belt is the most vulnerable element, determining the accuracy and reliability of the unit.
Steering mechanism manufacturers
Two suppliers' racks were installed on the BMW F10:
- ZF LS GmbH
- One of the largest suppliers of EPS for BMW.
- Uses a more massive gearbox.
- The racks often have a larger number of internal adjustment points.
- More common on diesel and AWD models.
- ThyssenKrupp Presta
- Characterised by a lighter design.
- Slightly different belt profile and encoder placement.
- Mostly P2VH active racks.
Racks are not always interchangeable between manufacturers, even with similar vehicle VIN numbers. The difference lies in the calibration, operating logic and encoder parameters.
Features of BMW EPS rack repair
Unlike hydraulic systems, the BMW F10 electric rack includes:
- a DC electric motor;
- a gearbox (mainly worm gear);
- encoders (optical or magnetic);
- a control module (ECU);
- torque sensors;
- belt drive.
Repair requires:
- specialised tools for disassembly;
- software for testing;
- accurate measurement of belt tension and gear engagement.
- EPS load bench (such as the MS521 used by STS);
Without access to diagnostic parameters and calibration tables, it is almost impossible to perform a quality repair.
Typical problems
In fact, the F10 rails have inherited all the typical problems and malfunctions of the E-series, namely:
- torque sensor malfunctions;
- EPS control unit failures;
- knocking, rattling or noise when turning the steering wheel.
Added to these are broken drive belts on the gears – as already mentioned, the most unreliable elements of the design. It is a loose or damaged belt that causes clicking when turning the steering wheel. Knocking on bumps indicates worn bushings or guides, while torque or torsional force errors are caused by malfunctioning encoders or sensors.
How to repair racks: OEM solutions versus alternatives
Official BMW service centres, like most car manufacturers, consider the electric steering rack to be a non-repairable unit, so if individual components fail, they usually recommend complete replacement. The price of a new unit ranges from €2,500 to €5,000 on average, depending on the configuration. For many owners of used cars of a respectable age, this does not make sense. An alternative is professional restoration, which can save up to 70% of the cost.
Restoration involves:
- replacement of all rubber and metal elements;
- installation of a new belt;
- checking/repairing encoders;
- calibrating the ECU for the specific configuration of the car.
The need for precise adjustment
In addition to mechanical assembly, the rack requires three important adjustments:
- Worm-rack engagement. Even 0.01 mm of incorrect pressure causes excessive backlash or jamming.
- Belt tension. Insufficient tension leads to vibrations, excessive tension leads to premature wear.
- Zero position torque calibration. This is critical for the operation of DSC, LKA, and adaptive cruise control functions.
Problems with poor-quality repairs
Most BMW electric steering rack models have a fairly simple design at first glance, which can create the misleading impression that they are easy to repair. In fact, these units are quite easy to disassemble, but reassembly, on the contrary, requires not only attention to detail, but also great skill. F10 steering racks must be assembled using the manufacturer's technology, with the use of special tools and in compliance with all tightening torques. Therefore, the restoration of these high-tech units should in no case be entrusted to novice mechanics who do not have sufficient qualifications and experience.
Common mistakes when repairing BMW F10 steering racks
- Installing non-standard belts (most often from power tools) leads to noise during operation and their rapid wear.
- replacing sensors or electronic components of the ECU, as well as any interference with the electronics of the unit without subsequent calibration, causes errors and incorrect operation of the rack;
- using non-original seal kits can lead to leaks after just 5–10 thousand kilometres of mileage.
In addition, difficulties arise due to the fact that many components (especially torque sensors, encoders, ECUs) do not have catalogue numbers because they are intended for installation only at the manufacturing plant.
Step-by-step repair process
- Diagnostics of the steering rack using a scanner via OBD/ISTA.
- Removal of the rack from the car (repair of the already removed unit is possible).
- Disassembly, defect detection.
- Cleaning of all components (using a sandblasting machine).
- Replacement of damaged mechanical elements: belt, bushings, bearings.
- Checking the electronic unit.
- Replacing its components if necessary.
- Assembly with adjustment.
- Test on the stand.
- Installation on the car.
- Calibration of the angle, torque, and steering wheel alignment.
What usually changes
- Belt. Regardless of the condition of the old one, new consumables must be installed.
- Seals. As in the previous case, all seals and gaskets are replaced with new ones from the repair kit.
- Bushings. We replace worn ones or those that are most prone to wear (also included in the repair kit).
- Encoders. They are checked and sometimes repaired.
- ECU.
- The unit is not always replaced, only when necessary, when it cannot be or is not advisable to repair it.
How STS Warsaw repairs BMW F10 rails
STS Warsaw is one of the few services in Poland that specialises in the repair and maintenance of high-tech car components, in particular BMW electric steering mechanisms. The main advantages of the workshop:
- Test benches manufactured by our own brand, MSG Equipment. MS521 — simulates load, allows you to check the operation of the rack ‘in dynamics’ (at speed, under load). The MS561 PRO tester allows you to test torque sensors, position sensors, ECUs, and gears.
- Quality control and access to unique spare parts, including repair kits of our own assembly.
- A 6-month warranty that we provide on all work performed and components.
- Exchange fund. A large number of refurbished components, which are always in stock, allows for the immediate replacement of the rack with a refurbished one, which is almost as good as a new unit.
Why STS Warsaw is the right choice
- Many years of experience in restoring EPS in cars.
- Modern equipment.
- Precise adjustment and testing.
- Original components or components refurbished using factory technology.
- Warranty and support.