Checking the EGR valve: is it working?
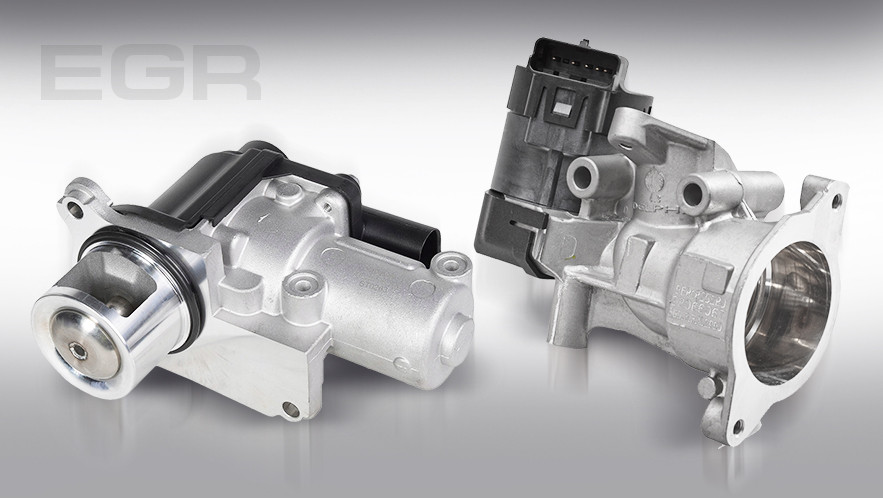
The EGR valve is an important component of a vehicle's emissions control system. Its main function is to partially return exhaust gases to the intake manifold, which reduces the combustion temperature of the fuel and reduces nitrogen oxide emissions. But what should you do if you suspect a malfunction? Find out how to check the EGR and determine if it is working properly.
Design and types of valves
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is designed to return part of the exhaust back to the engine instead of into the atmosphere, reducing nitrogen oxide emissions. It connects the exhaust tract to the intake manifold after the throttle valve via a special channel. When the engine is idling or running at low revs, this allows some of the exhaust gases to be returned to the combustion chamber.
EGR valves are mostly installed on diesel vehicles. They are divided into three main types:
- Pneumatic – opens due to a change in pressure in the intake manifold. This type was used on older car models.
- Pneumatic-electric – similar in design to the pneumatic type, but controlled by an electronic engine control unit.
- Electric – equipped with its own servo drive, the time and degree of opening are controlled by an electronic control unit.
How an EGR valve works
An EGR valve consists of the following main components:
- Valve body – acts as a frame that holds all the elements in place.
- Bypass valve – a mechanism that opens or closes the exhaust gas supply channel.
- Valve actuator – can be vacuum or electromagnetic.
- Valve position sensor – used in electronic valves for feedback to the engine control unit.
- EGR cooler (in some models) – reduces the temperature of the recirculated gases before they enter the intake manifold.
The design of the EGR valve can vary significantly depending on the model and year of the vehicle. It can be either a large assembly similar to a throttle valve or a compact element similar in size to an idle speed regulator.
Signs of EGR malfunction
Unfortunately, the exhaust gas recirculation valve only works effectively under ideal conditions. Poor fuel quality, difficult operating conditions, and other unfavorable factors cause it to fail quickly. This usually manifests itself as the valve not opening or closing completely, i.e., sticking in one position. This situation can cause a number of problems in the engine, as exhaust gases are constantly entering it.
Before checking whether the EGR valve is working properly, remember the main symptoms of a malfunction:
- Unstable engine speed when idling
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Loss of power and dynamics
- Increased fuel consumption
- Jerking during acceleration
- Smoky exhaust (black or white smoke) with an unpleasant odor
- Check Engine light on the instrument panel
- Detonation or misfiring
The most common malfunctions
The EGR valve is designed to be closed more often than it is open. However, this is still enough for problems to arise. The main causes of EGR valve malfunctions are usually:
- Coking and contamination of the valve with carbon deposits
- Breakage or wear of the membrane
- Failure of the solenoid valve
- Damage to the position sensor
What are the risks of a faulty EGR
If the fault is not rectified, it can lead to more serious problems:
- Reduced engine performance
- Increased emissions of harmful substances
- Increased wear on engine components
- Possible engine overheating
In addition, even if the EGR system is working correctly, its operation can also have negative consequences:
- Mixing of hot exhaust gases with cold air. This reduces the efficiency of the intercooler, which can lead to a loss of engine power.
- Increased carbon buildup. Soot particles from the exhaust gases settle in the intake manifold and on the valves, gradually reducing their flow capacity.
- Accelerated engine oil contamination. Due to the recirculation of exhaust gases, soot particles enter the combustion chamber, leading to faster engine oil aging.
- Uneven fuel combustion. Excess exhaust gases can disrupt the combustion process, especially at low revs.
How to check if the EGR valve is working
What you can see yourself
With at least a basic knowledge of the structure of a car, the driver can try to identify the problem on their own. First, visually inspect the EGR valve:
- Check for carbon deposits or clogging
- Check the tightness of the connections
- Make sure there are no cracks or mechanical damage
Diagnostics
For a more detailed check, the following methods can be used:
- Check the EGR valve with an OBD-II scanner – detect errors related to the EGR (most often this is code P1405)
- Check the vacuum valve – check the operation of the membrane using a vacuum pump
- Multimeter check – measuring the voltage on the electronic valve
- Mechanical testing – removing the valve and checking its operation manually
It is important to know that it is not always the valve itself that causes malfunctions. There are situations where the problems may be related to other components: for example, if the vacuum hose is cracked, the scanner readings will be the same. Therefore, for quality advice and repairs, it is best to contact professionals – preferably STS.Parts in Warsaw. The specialists at this workshop have many years of experience in repairing high-tech car components, so they know how to check the EGR valve and repair it.
How to repair the EGR valve
You cannot drive with a faulty valve; the problem must be solved as soon as possible. There are two ways to do this: repair or remove/deactivate it.
Valve repair – pros/cons
If the valve is not mechanically damaged, it can be cleaned and returned to working order.
Pros
- Restores operation without replacement
- Lower cost compared to buying a new valve
Cons
- May not work if significantly worn
- Temporary solution if the problem recurs
Deactivating the EGR valve – pros and cons
Some car owners decide to completely disable the valve either programmatically or mechanically. On used cars with high mileage, this method has proven to be the most effective.
Pros
- Reduced risk of manifold clogging
- Lower repair costs in the future
Cons
- May lead to increased emissions
- May be illegal in some countries
Should the valve be physically disabled and when
Physical disabling of the EGR valve (installing a plug) may be justified in the following cases
- If the valve is constantly malfunctioning
- If the car is used without a catalytic converter
- If software disabling has not worked
Preventing EGR valve malfunctions
To avoid problems with the EGR valve, it is recommended to:
- Use high-quality fuel
- Clean the intake system regularly
- Diagnose the EGR from time to time
- Replace the valve according to the manufacturer's recommendations
- Avoid frequent short trips where the engine does not warm up to operating temperature
By following these tips, you can keep your EGR valve in good working order and avoid the unpleasant consequences of its failure.