How an alternator works in a car: construction, symptoms of a broken one
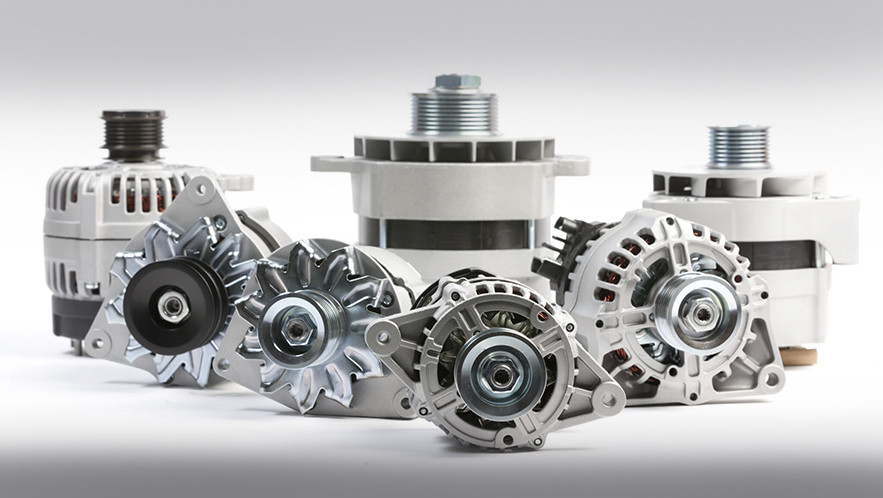

It is commonly believed that the source of electric current in a car with an internal combustion engine is the battery. In reality, the battery only provides stored energy for a few seconds while the starter is running, after which the generator kicks in. The generator is the real electricity producer, supplying the entire car, including the battery, which has had time to discharge during engine start-up. Let's take a look at how a generator works in a car, what it is for, how to identify a malfunction, and what to do if problems arise.
What is a generator for?
A generator can be called the heart of a car's electrical system without exaggeration. The task of this device is to convert the mechanical energy produced by a gasoline or diesel engine into electrical energy. An alternator performs a number of important functions:
- Charges the battery while the engine is running, preventing it from discharging.
- Supplies power to all electrical systems (lighting, multimedia, air conditioning, etc.).
- Maintains a stable voltage in the on-board network.
Most often, this unit is connected in the form of an attachment: on an easily removable bracket with a belt drive from the engine pulley. This design exists on both conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and MILD hybrids.
Structure and principle of operation
This device is actually the same age as the car, and its design has changed little since it was developed and patented by Nikola Tesla in 1891. Here is how a generator is arranged and what it consists of:
- Rotor – a moving part that rotates under the influence of a belt and creates a magnetic field.
- Stator – a stationary part in which alternating current is generated. It usually consists of an insulated steel frame with wire wound around it.
- Rectifier (diode bridge) – converts alternating current into direct current. The most commonly used is a single-phase Gretz bridge with four diodes assembled in a frame.
- Voltage regulator – controls the current level for stable operation of the electrical system. The charging relay allows the voltage to be kept at approximately the same level.
- Bearings – ensure smooth rotation of the rotor, prevent overheating and jamming.
- Brush assembly – transmits electrical current to the rotor winding. Responsible for transmitting electrical current from the rotor to the stator. Mostly made of graphite or a mixture of graphite and copper.
The principle of operation of an AC generator has also remained unchanged:
- The crankshaft of the engine rotates the generator rotor via a belt stretched between the pulleys.
- The magnetic field of the rotor from the rotation creates an alternating current in the stator.
- The rectifier converts the alternating current into direct current, as the car's electrical system has clearly marked “plus” and “minus” terminals.
- The voltage regulator maintains a stable voltage level for the correct operation of electrical appliances, preventing them from breaking down.
The most common generator faults
Generator faults can vary, but they all boil down to a malfunction and, as a result, a lack of battery charge. Here are the most common problems:
- Wear or damage to the brushes.
- Failure of the voltage regulator.
- Bearing failure.
- Breakage or slippage of the drive belt.
- Failure of the diode bridge.
Signs of serious damage
A broken generator will not cause the engine to stop immediately or the car to suddenly immobilize, but despite this, the situation cannot be called normal. If the generator does not supply the required current, power is supplied from the battery, which does not receive a charge in return and eventually discharges. The operating time in this case depends on the type of vehicle (diesel/gasoline) and the number of consumers turned on, but in general it is usually short. Therefore, the driver must quickly identify and eliminate the cause of the malfunction.
Signs of a damaged generator are usually as follows:
· A red battery icon on the instrument panel.
- Dim or flickering headlights.
- Problems with electrical systems (radio, air conditioning, power windows).
- Unusual noises (grinding, whistling) under the hood.
- Complete battery failure.
It is important to remember that the above symptoms may also indicate malfunctions of other components and systems. For example, a charging indicator may be caused by a faulty signal relay or a broken circuit.
What are the possible causes of generator failure?
The main causes of generator failure are:
- Natural wear and tear of parts.
- Overheating due to excessive load.
- Moisture or dirt getting inside the device or on its drive belt.
- Poor quality parts or use of incompatible spare parts.
- Improper operation or installation.
In addition, such trivial reasons as insufficient belt tension, stretching or deformation of the belt, and/or poor fastening of the device or pulley can cause malfunctions in the generator.
What to do if you have problems with the generator
If you notice signs of generator malfunction, you must:
- Check the condition of the battery and contacts.
- Make sure that the generator belt is not loose or broken.
- Contact a car service center for diagnosis and repair.
It is strongly recommended not to check the generator's performance using the old-fashioned method of disconnecting the battery terminal. Yes, indeed, if the device does not supply the current required by the car, it will be noticeable – the engine will stall. However, unlike older carburetor cars, modern cars have a lot of electronics, for which such a voltage surge can be fatal.
Therefore, you should only check the generator yourself using a multimeter connected to the battery terminals. When the engine is running, the voltage at the battery terminals should be between 13.8 and 14.4 V. If the voltage is below 13.8 V, this may indicate that the generator is not charging.
Is it worth repairing the generator?
The answer to this question depends on the design of the unit and the extent of the malfunction. Repairing the generator may be advisable in the following cases:
- If the problem is not complicated: related to the brushes, voltage regulator, or diode bridge.
- If the generator bearings need to be replaced and are available.
- If repair is significantly cheaper than replacement.
Note that it is not worth replacing a faulty generator with a used, unrepaired unit with a dubious history—its actual condition may turn out to be not much better than the old one.
When to replace the generator
Replacing the generator in a car should be considered if:
- Diagnostics have revealed critical damage.
- The generator is unstable even after repair.
- The cost of repair is close to the price of a new generator.
Another relatively inexpensive solution to the problem is to replace the damaged generator with a high-quality refurbished one from STS's large exchange fund.
How much does it cost to replace a car generator
The cost of replacement depends on:
- The make and model of the car.
- The type of alternator.
- Whether you choose a new or refurbished alternator.
- The cost of labor.
On average, the price ranges from $150 to $450.
How to prevent alternator failure
To avoid problems with the alternator, you should:
- Regularly check the condition of the generator belt.
- Diagnose the electrical system in a timely manner.
- Avoid overloading the car's electrical appliances.
- Use only high-quality spare parts.
Where is the best place to repair a generator in Warsaw
If you have problems with your generator or other electrical systems in your car, STS in Warsaw is the best choice.
Why you should choose us
- Many years of experience – our experts have in-depth knowledge and practical experience in generator repair.
- Qualified specialists – certified technicians perform repairs quickly and efficiently.
- Modern equipment – we use professional diagnostic and repair equipment.
- Warranty on work – STS provides a 6-month warranty on generator repairs.
Contact STS in Warsaw for high-quality generator repairs and to avoid problems in the future!